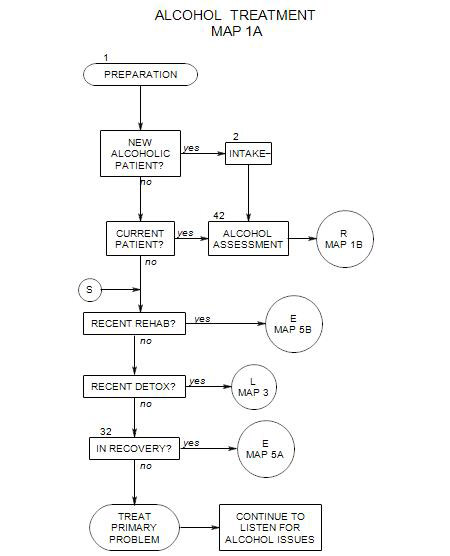
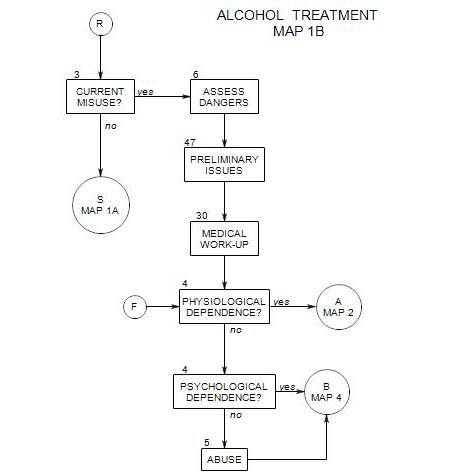
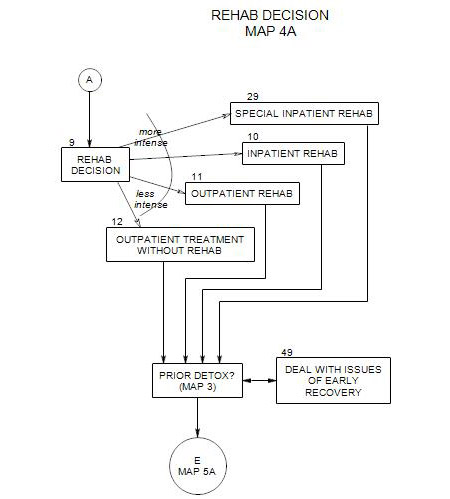
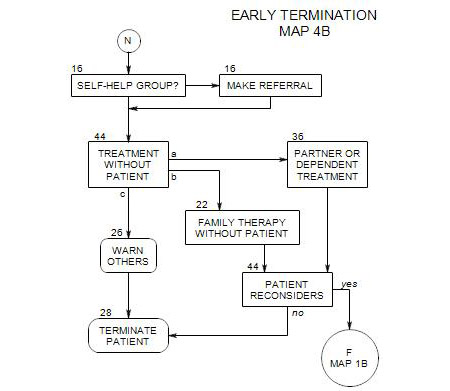
12. OUTPATIENT TREATMENT WITHOUT REHABILITATION
- Rehabilitation is discussed in Section 9 on Map 3.
Patients who choose this option are not exposed to the intensity of the various levels of rehabilitation. They return to their regular lives immediately, with some form of outpatient psychotherapy.
Some patients, especially those with prior rehabilitation experience, may be prepared for the cravings, disorientation, chronic pain, sleep issues, and so on, of early recovery. They know that it will take time for the symptoms to abate, and they are prepared to put up with those symptoms until they feel better. For them, rehab might be an unnecessary luxury.
Others may have difficulty dealing with issues of early sobriety. Common symptoms seem too much, and they don’t know how to handle them. They are at immediate and constant risk for relapse, as they try to cope with their own limits and urges. They may also miss the separation from everyday life that rehab affords, possibly jumping right back into the situations and pressures associated with their alcohol misuse. With these patients, the therapist may need to compensate for the absence of rehabilitation with more intensive primary treatment [ Section 14 ] and/or more adjunctive services [Section 19]. Some arrangement should be made to check in with the patient on a regular basis about recovery symptoms and the temptation to relapse. Questions should be specific to symptoms that the patient is experiencing or has had previously. See “Symptoms and Issues of Early Recovery” [ Section 27 ] and “Signs of Impending Relapse [ Section 33 ] for more on this issue.
Someone needs to manage and coordinate services and the patient’s participation in them. Typically this can’t be the patient, whose self control and judgment are compromised. It is likely to fall on the primary therapist to set up lines of communication with other providers and strategies for coordinating the services offered and encouraging patient participation.